| What to test for | Implications |
|---|---|
| Compaction | Root penetration and water infiltration |
| Bulk Density | Seedling emergence and air circulation of the soil |
| Structural Stability | Aggregate stability in water is an indicator of infiltration and erosion |
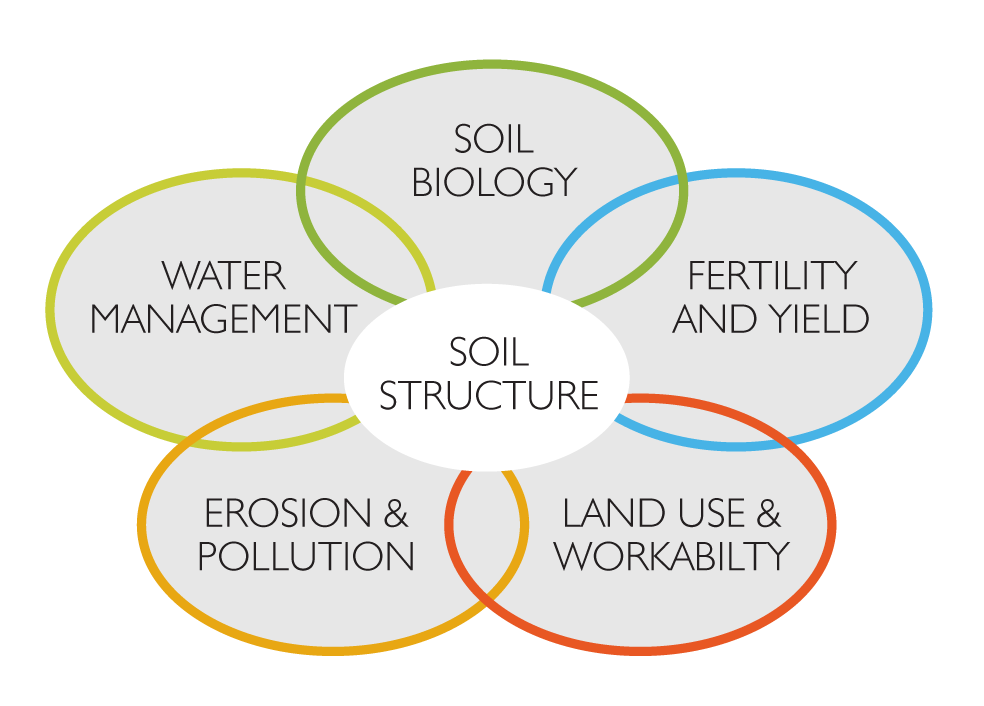
Why Is Good Structure Important?

On Farm Testing
Penetration resistance
use a penetronmeter to measure sub-surface compaction – important for drainage and restricting root growth
(VESS) visual evaluation of soil structure
Click here for more information
• Structure quality• Size and appearance of aggregates
• Visible porosity and roots
• Appearance after breaking up the soil
• Distinguishing features
• Appearance and description of fragments
Slake test
Slake test will indicate the stability of the soil aggregate, resistance to erosion and impact of management in soil health
Click here for more information
(UK version coming soon!!)

Lab Testing
Particle analysis
proportion of sand : silt : clay reported as fractions
Bulk density
is an indicator of compaction and takes the dry weight of soil divided by volume
Particle size analysis
proportion of different size particles
Click For Soil Testing Labs And Services



